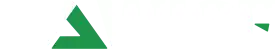Tilapia is a fast-growing fish with strong adaptability, making it a popular choice among fish farmers. To raise healthy and profitable tilapia, feed selection plays a crucial role. With feed accounting for more than 60% of total farming costs, understanding the nutritional needs of tilapia at each growth stage and selecting the right feed is essential for improving productivity and maximizing profits.

Understanding the Nutritional Needs of Tilapia
Biological Characteristics and Dietary Habits
Tilapia is a highly adaptable omnivorous fish, native to Africa and now farmed worldwide. It can survive in freshwater, brackish water, and low-oxygen environments. Throughout its growth stages, tilapia's dietary preferences shift:
- Fry stage: Primarily feed on zooplankton like rotifers and cladocerans.
- Juvenile stage: Favor phytoplankton, organic debris, and formulated feeds.
- Adult stage: Stable feeders with increased protein and energy needs to support reproduction.
Digestive System Structure and Feeding Habits
Tilapia has a relatively simple but versatile digestive system, with a long intestine suited for digesting various foods. Active during the day and resting at night, they benefit from multiple small feedings daily, especially when water temperatures are optimal.
Water Temperature and Appetite
Water temperature directly influences tilapia's metabolic rate and feeding behavior. The optimal feeding range is 26°C to 30°C. Below 20°C, feeding slows down; above 35°C, stress may lead to reduced or ceased feeding. Therefore, flexible adjustments to feeding strategies based on seasonal changes are essential.

Nutritional Needs at Different Growth Stages
Tilapia has different nutritional needs at various stages of growth, especially for protein and fat levels:
| Growth Stage | Weight | Crude Protein | Fat | Key Focus |
| Fry | 0.02–1.0g | 45–50% | 5–10% | High protein, easy digestibility, immune enhancers |
| Fingerlings | 1.0–10.0g | 35–40% | 5–8% | Balanced amino acids, mineral supplementation |
| Juveniles | 10.0–25.0g | 28–35% | 4–6% | Fast growth, feed conversion efficiency |
| Adult Fish | >25g | 28–30% | 4–6% | Fat management |
(Source: Nile tilapia - Nutritional requirements & Feed for tilapias)
Protein and fat are the key nutrients that drive tilapia growth and health. Adjusting their levels based on the fish's growth stage helps farmers boost feed efficiency and improve results.
Scientific Formulation of Feed Ingredients
To meet tilapia's changing nutritional needs, formulating feed with the right balance of ingredients is crucial.
Core Nutritional Elements in Tilapia Feed
Balanced nutrition-including protein, fat, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals-is vital for healthy tilapia growth.
| Nutrient | Primary Function | Common Sources |
| Protein | Muscle building, weight gain | Fish meal, soybean meal, cottonseed meal |
| Fat | Energy sources, reducing protein waste | Fish oil, vegetable oil |
| Carbohydrates | Additional energy, cost savings | Cornmeal, wheat flour |
| Vitamins | Immunity boosts stress resistance | Vitamin premixes |
| Minerals | Bone development, metabolic balance | Calcium, phosphorus, zinc, iron |
Functional Feed Additives
Appropriate use of functional additives in tilapia fish food can enhance immunity, improve gut health, and boost stress resistance.
| Additive Type | Function |
| Probiotics | Improve gut health and digestion |
| Enzymes | Break down feed for better absorption |
| Anti-stress agents | Resist temperature and water quality changes |
| Immune boosters | Strengthen disease resistance |
How to Choose the Right Type of Tilapia Feed
Understanding the differences in feed texture and buoyancy helps in selecting the right type based on fish size, growth stage, and farming environment.
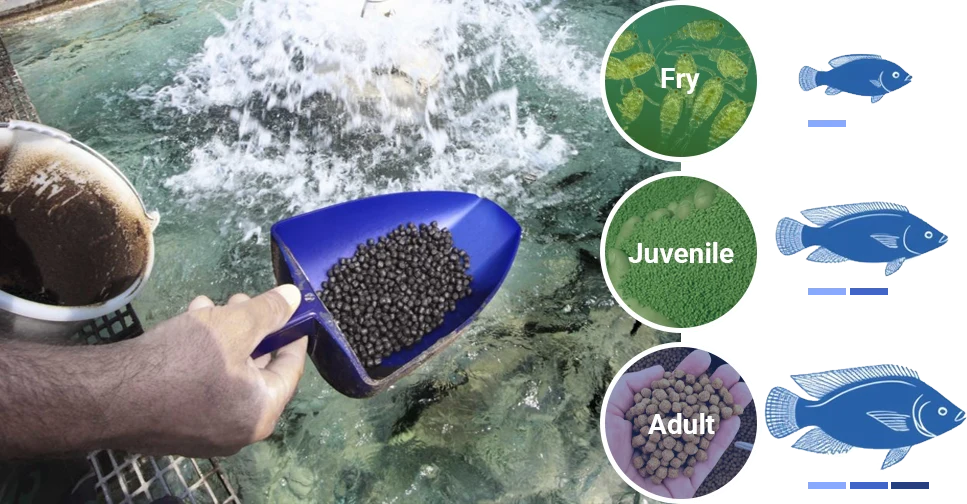
| Feed Type | Buoyancy | Key Features | Best Application |
| Powder feed | Suspended | Rapid dispersion, good palatability, water pollution risk | Fry with weak feeding ability |
| Sinking pellet feed | Sinks | High density, suitable for bottom-feeding | Flowing water or cage farming |
| Floating fish feed | Floats | Saves feed, easy management | Pond farming, easy feeding observation |
| Extruded floating feed | Mostly floats | Easily digestible, stable in water | High-density ponds, precision feeding |
Tilapia fries thrive on powder feed, while juveniles and adults benefit more from pellet or extruded floating feed. Choosing between floating feed and sinking options depends on farm management preferences and environmental conditions.
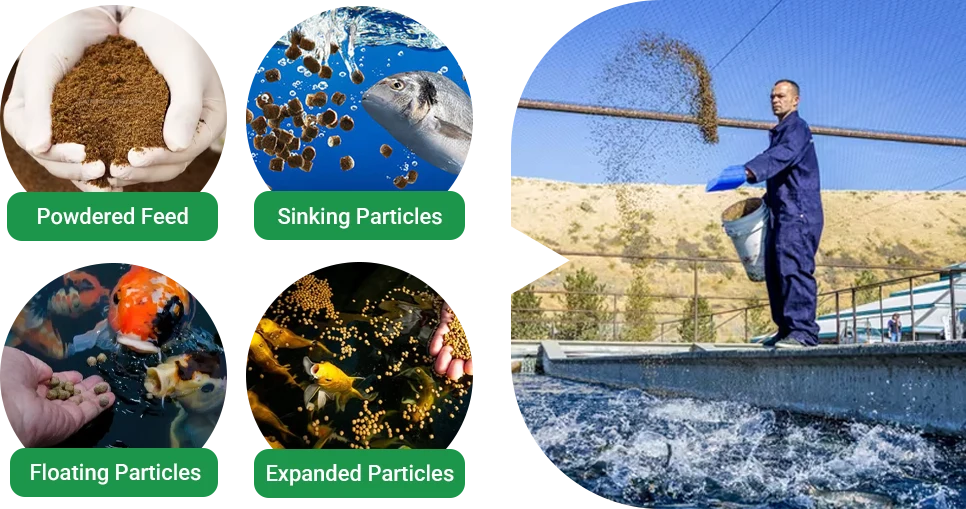

Key Technologies in Feed Production
The processing techniques of tilapia feed not only determine its appearance and shape but also directly affect its nutritional value, palatability, and utilization rate. Using the right fish feed machine and production methods is fundamental to ensuring consistent quality.
Powder Feed
Powder feed is mainly used for tilapia fry. It requires fine grinding, uniform mixing, and anti-caking treatments. Proper fish feed making machine setups are essential to avoid issues like water pollution from excess powder.
Pellet Feed
Pellet feed, often produced using a fish feed pellet machine, is the most common form for tilapia. Controlling pressing temperature, mold aperture, and moisture content is critical. Proper density adjustments determine if the pellets are floating or sinking.

Extruded Feed
Produced with a fish feed extruder machine, extruded feed undergoes high-temperature, high-pressure treatment, resulting in floating feed with superior digestibility and water stability. Ideal extrusion temperatures are between 100-130°C to balance ingredient cooking and nutrient preservation.
| Growth Stage | Recommended Pellet Diameter |
| Fry | ≤0.5 mm |
| Fingerling | 0.8–2.5 mm |
| Adult | 3–5 mm |

Practical Feeding Management Strategies
Effective feeding management can significantly enhance feed conversion ratios, lower farming costs, and promote healthy fish growth.
| Aspect | Recommended Practice |
| Water temperature | Maintain 26°C–30°C |
| Feeding frequency | 3-5 times daily for juveniles, 2 times for adults |
| Daily feed amount | 3%-6% of total fish weight; reduce in cold weather |
| Feeding observation | Ensure all feed is consumed within 15-20 minutes |
| Feeding method | Fixed time and location; multiple small feedings; use floating fish feed for easy monitoring |
For large-scale operations, adopting automatic feeding systems can improve efficiency and precision, helping maximize the performance of every batch of tilapia.
Common Issues and Solutions
Even with the best feeding practices, some challenges are hard to avoid. Here are some common issues in tilapia farming-and how to deal with them.
Causes and Solutions for Refusal to Eat
| Cause | Solution |
| Deteriorated or unpalatable feed | Use fresh, high-quality tilapia fish food |
| Incorrect pellet size | Match feed size to fish size |
| Nutritional imbalance | Adjust fish feed formulation to meet nutritional needs |
| Sudden feed changes | Transition gradually between old and new feed |
| Improper feeding methods | Optimize feeding times and amounts |
Handling Abnormal Feces
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Suggested Action |
| White, flaky feces | Excess protein or indigestion | Reduce protein level, add probiotics |
| Stringy feces | High fiber content, poor digestibility | Adjust feed formulation to lower fiber |
| Undigested feed in feces | Pellets are too large or too hard | Choose appropriate pellet size and hardness |
Managing Growth Discrepancies
| Problem | Adjustment |
| Size differences within fish groups | Use varied pellet sizes |
| Severe competition during feeding | Increase feeding points, ensure even distribution |
Tilapia Feed Market Analysis
Tilapia farming is mainly concentrated in China, Indonesia, Egypt, Brazil, and Thailand, with China leading global production at 1.24 million tons per year ( FAO GLOBEFISH,2023 ). As the industry grows and local feed resources remain limited, countries like China, Egypt, the Philippines, Nigeria, and Brazil are increasingly relying on imported tilapia feed and raw materials. This rising demand is fueling the rapid development of the global tilapia supply chain.
Given the high cost and volatility of imported feed, many farmers are exploring producing their own tilapia feed using localized resources and equipment like fish feed extruder machines.
Selecting the right tilapia feed, mastering production techniques, and managing feeding scientifically are critical steps toward maximizing farming success.
To support farmers aiming for a fully integrated feed-to-fish production loop, we offer a range of fish feed pellet machines, fish feed making machines, and customized production lines. Feel free to contact us for more details and cooperation opportunities!